Steps to Register a Business or Company Legally – 2025 Complete Guide
Starting a business is exciting, but doing it legally, following rules, and registering properly gives you protection, credibility, and access to government schemes and funding. In 2025, many processes are digital, but you must know each step, document, cost, and compliance requirement. This guide walks you through how to legally register a business or company in India (or similar systems), what types to choose, required documents, comparison, timeline, costs, and tips.
Why Legal Business Registration Matters
Registering your business legally defends you from lawsuits, helps in obtaining licenses, loans, contracts, tax compliance, and builds trust among customers or partners.
- Legal recognition as a distinct entity
- Limited liability protection (in corporate forms)
- Access to government schemes, subsidies, and benefits
- Easier to open bank account, raise capital, issue invoices
- Better credibility with customers, vendors, investors
Choose the Right Business Structure
Selecting the correct legal form is critical—each has pros, cons, compliance requirements, and tax implications.
Sole Proprietorship
Owned and run by one person. Simplest form, with minimal registration, but the owner has unlimited personal liability.
Partnership / Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
Partnership involves two or more persons. LLP offers features of partnership plus limited liability protection for partners.
Private Limited Company
A separate legal entity with shareholders and directors. Must follow stricter compliance, but offers limited liability, easier capital raising.
Public Limited Company
A company that can invite public to subscribe shares. More regulations, more transparency, suitable if you plan large scale growth.
One Person Company (OPC)
A hybrid: a single person can form a company but enjoy benefits of limited liability. Useful for small entrepreneurs wanting corporate structure.
Major Steps to Legally Register a Business
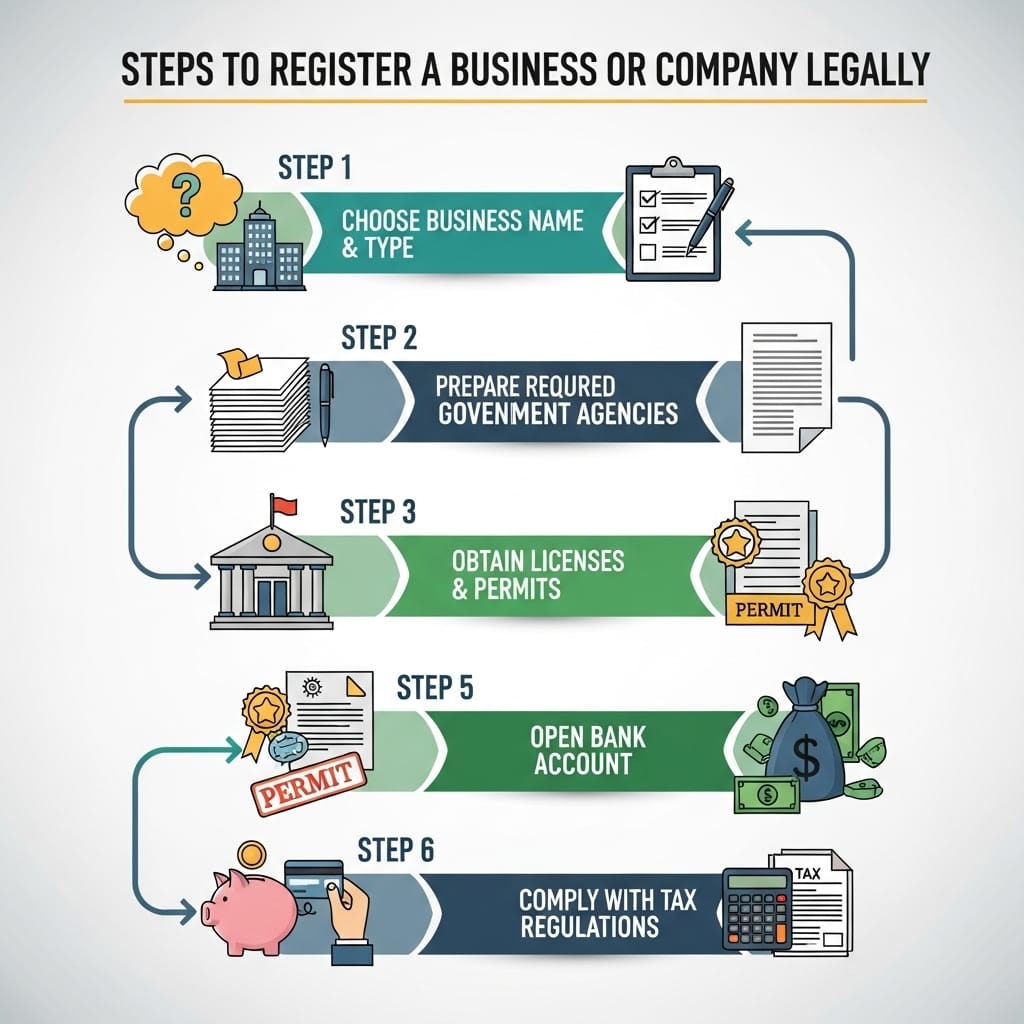
Step 1: Choose a Unique Name and Check Availability
Brainstorm a business name, check that no other entity uses it. In government registry, ensure name availability before proceeding.
Step 2: Decide State / Jurisdiction & Registered Office
You must specify where the registered office will be. Some compliance and taxation depend on the state or jurisdiction.
Step 3: Prepare Required Documents
Documents vary by structure but common ones include identity proofs, address proofs, passport photos, proof of registered address (rental agreement or lease, utility bills), PAN, and incorporation forms.
- Identity & address proof of owners/directors/partners
- Photographs
- Proof of registered office address
- Entry of directors/partners with consent letters
- Memorandum of Association (MOA) & Articles of Association (AOA) for companies
- Partnership deed (if partnership)
Step 4: Apply for Digital Signature & Director Identification (if needed)
For companies, directors must have digital signatures for online filing. Also, apply for Director Identification Number (DIN) or equivalent in your jurisdiction.
Step 5: Fill Incorporation or Registration Forms & Submit Online / Offline
Use the government portal (e.g. MCA in India) to fill incorporation application, upload documents, pay fees, and submit. Some jurisdictions also allow physical submissions.
Step 6: Verification, Review & Approval
After submission, registrar reviews documents, may ask for clarifications or corrections. Once satisfied, certificate of incorporation or registration is issued.
Step 7: Obtain PAN, TAN, GST Registration & Other Licenses
After legal registration, get your tax identity numbers like PAN, TAN, GST (if applicable), trade license, shop & establishment license, etc.
Step 8: Open a Bank Account & Start Business Operations
Use your incorporation certificate and identity documents to open a business bank account. Then you can legally start operations, sign contracts, issue invoices etc.
Comparison: Business Structures & Key Features
| Feature | Sole Proprietorship | LLP / Partnership | Private Limited Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liability | Unlimited personal liability | Limited liability for partners (in LLP) | Limited liability for shareholders |
| Compliance Requirements | Minimal | Moderate | High (annual filings, audits etc.) |
| Capital Raising | Limited to owner’s funds | Can bring in partners’ capital | Can issue shares, bring in investors |
| Perpetual Succession | No (business dissolves with owner) | Depends on partnership agreement | Yes (company continues regardless of changes) |
| Cost of Formation | Lowest | Moderate | Higher |
Timeline & Cost Estimates
Typical Timeline
- Name approval: 1–3 days
- Document preparation: 1–5 days
- Incorporation processing: 2–7 days (may vary with backlogs)
- Post‑registration tasks (pan, gst, licenses): additional few days to weeks
Estimated Cost Components
- Government registration / filing fees
- Digital signature / certificate cost
- Professional fees (if you hire consultant or CA / lawyer)
- Stamp duty, legal fees, notary costs
- License fees, GST registration charges
Common Challenges & How to Overcome
Name Rejection or Duplication
If your proposed name conflicts with existing names or is too generic, registrar may reject. Submit alternate names and ensure uniqueness.
Document Discrepancies
Mismatch in addresses, identity proof, or spelling errors cause rejection. Check carefully before submission.
Delay in Approvals
Backlogs, holidays, or regulatory scrutiny may delay incorporation. Be patient and follow up with registrar if needed.
Non‑compliance After Registration
Ignoring required filings, audits, tax returns can lead to penalties. Maintain a compliance calendar from day one.
Tips for Smooth Business Registration
- Plan names and backup alternatives in advance
- Gather all documents beforehand and scan clearly
- Use correct formats and follow instructions strictly
- Hire or consult a chartered accountant or company secretary if possible
- Keep digital copies and backups of all filings
- Monitor email or portal for queries or remarks by registrar
Conclusion
Legally registering a business or company ensures your venture starts on a solid foundation. While the process may seem complex, breaking it down into clear steps—choice of structure, document preparation, registration submission, post‑registration compliance—makes it manageable. Use this guide to navigate registration, choose the right form, comply with requirements, and begin your business journey with confidence.